Gaywallet (they/it)
I’m gay
- 177 Posts
- 576 Comments
 3·3 days ago
3·3 days agovery cute!
compress the image first, there’s a max upload size and I think a max pixel size (I forget)

 4·4 days ago
4·4 days agoYes, but if a review board were to sign off on them and then someone managed to significantly hurt or damage themselves, one could theoretically apply some of the blame to the review board for not doing their job to ensure that a study was safe. The whole idea of having ethics as a part of the review board was born of some of the studies they used to sign off on that were ultimately problematic and resulted in seriously damaging some individuals, such as minorities and kids.

 6·4 days ago
6·4 days agoSorry by experimental what I meant here is something which is not ready to be tested in humans - this scientist was skipping a bunch of the necessary steps to show this is a safe thing to do (in lab grown cells first, for example) to proceed to human experimentation.

 17·5 days ago
17·5 days agoEthically speaking, we should not be experimenting on humans, even with their explicit consent. It’s not allowed by any credible review board (such as the IRB) and in many countries you can be held legally liable for doing experiments on humans.
With that being said, there have been exceptions to this, in that in some countries we allow unproven treatments to be given to terminal patients (patients who are going to die from a condition). We also generally don’t have repercussions for folks who experiment on themselves because they are perhaps the only people capable of truly weighing the pros and cons, of not being mislead by figures of authority (although I do think there is merit of discussing this with regards to being influenced by peers), and they are the only ones for which consent cannot be misconstrued.

 1·10 days ago
1·10 days agoMy dude, I told you to chill and take a step back. People were reporting you for being confrontational. I flagged my comment to help you understand that this was me helping you understand how we do things on Beehaw. If you think someone reminding you of the rules, asking you to take a step back, asking you to not be confrontational and doing their best to treat your comment with good faith and providing you educational material is “rude and condescending” or that it is “talking down to others” then you’re probably not a good fit for this instance.
I’m going to time you out from our instance for 7 days. Please take that time to reflect. If you repeatedly show this behavior on our instance, you may find yourself with longer timeouts or even being removed.

 5·11 days ago
5·11 days agoHey there, I’ve removed this comment because it reads as rather aggressive (and was reported for such). Maybe take a step back and re-assess if you’re treating others with good faith and be(e)ing nice.
that still doesn’t make this about colonialism because this is about capitalism.
FYI- there is wide overlap between these two and they are not mutually exclusive. If you’re unfamiliar with the use of these terms, you should ask how they are defined or how they are being used, rather than pushing a pedantic lens on the words definition.

 2·13 days ago
2·13 days agoGreat article, thanks!

 13·16 days ago
13·16 days agoyou should filter out irrelevant details like names before any evaluation step
Unfortunately, doing this can make things worse. It’s not a simple problem to solve, but you are generally on the right track. A good example of how it’s more than just names, is how orchestras screen applicants - when they play a piece they do so behind a curtain so you can’t see the gender of the individual. But the obfuscation doesn’t stop there - they also ensure the female applicants don’t wear shoes with heels (something that makes a distinct sound) and they even have someone stand on stage and step loudly to mask their footsteps/gait. It’s that second level of thinking which is needed to actually obscure gender from AI, and the more complex a data set the more difficult it is to obscure that.

 14·27 days ago
14·27 days agoWe weren’t surprised by the presence of bias in the outputs, but we were shocked at the magnitude of it. In the stories the LLMs created, the character in need of support was overwhelmingly depicted as someone with a name that signals a historically marginalized identity, as well as a gender marginalized identity. We prompted the models to tell stories with one student as the “star” and one as “struggling,” and overwhelmingly, by a thousand-fold magnitude in some contexts, the struggling learner was a racialized-gender character.

 1·29 days ago
1·29 days agoThis isn’t related to science, feel free to repost in news
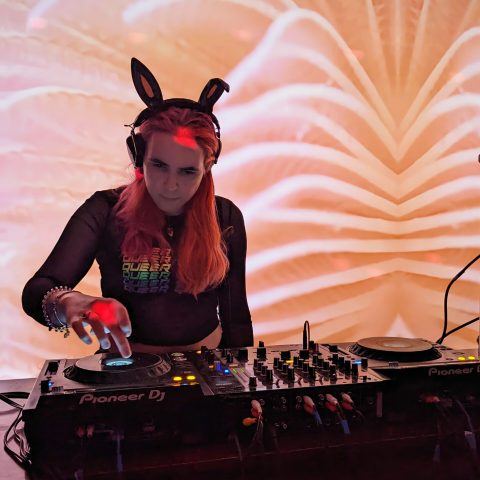
Gig went great, lots of attendance, we hit bar goal so they invited us back, my set ended up being peak crowd and everyone was dancing instead of chatting in the front room, got a ton of compliments including a “I don’t normally like EDM but your set was great” which is always a treat
Had a wonderful weekend with a few great dates, continued good vibes into this week. I play a DJ gig tonight with a crew that I’m involved with the organization of, we’re trying to find a weekday night to regularly takeover and I’m excited to see what kinda turnout we get.

 2·1 month ago
2·1 month agoGuess I’ll have to wait for the book, but that title might be misleading. It sounds like they had discussions about the process, in light of Trump being… well, Trump. Not that Trump ever ordered anything to do with nuclear weapons and Milley preventing said action.

 2·1 month ago
2·1 month agoAn interesting article, thanks for sharing. I’ve been to SLC a few times. I used to have a trans friend who lived out there. Unfortunately she had a medical complication that lead to her passing away, but I always found the city a fascinating enigma. I went back out there the other year for a conference and the little gayborhood was still just as gay and had fantastic food.

 2·1 month ago
2·1 month agoIf you wish to discuss the controversy, feel free to make a post or link to an article. I’m personally not interested in hosting a link to these weirdos.

 11·2 months ago
11·2 months agoI find NFC stickers often require an annoyingly close connection (unless it’s a rather large antenna) and can be particularly finicky with certain cases and other attachments people put on phones. Realistically they both take approximately the same amount of time and it’s way cheaper to print a tag than it is to buy a single NFC sticker

 5·2 months ago
5·2 months agoYou’re welcome to have your own beliefs.
You are not, however, welcome to use those beliefs to invalidate someone else’s lived experience.

 24·2 months ago
24·2 months agoMy fav application is scanning with a phone to immediately get on wifi
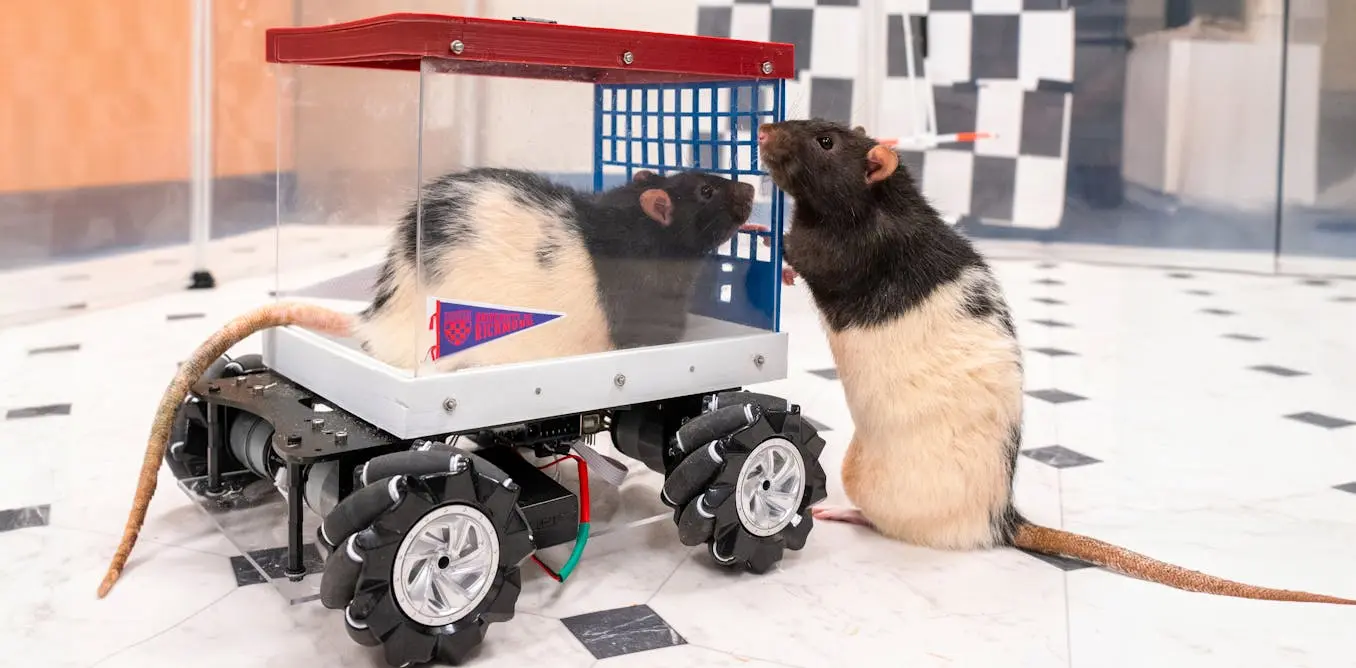















It’s a big step up from literally drowning lab rats as an experiment, but we’ve got a long way to go before we get even reasonably ethical with lab animals 😔
To be fair if anyone was gonna not kill them when they’re done, this lab seems like they might be the ones.